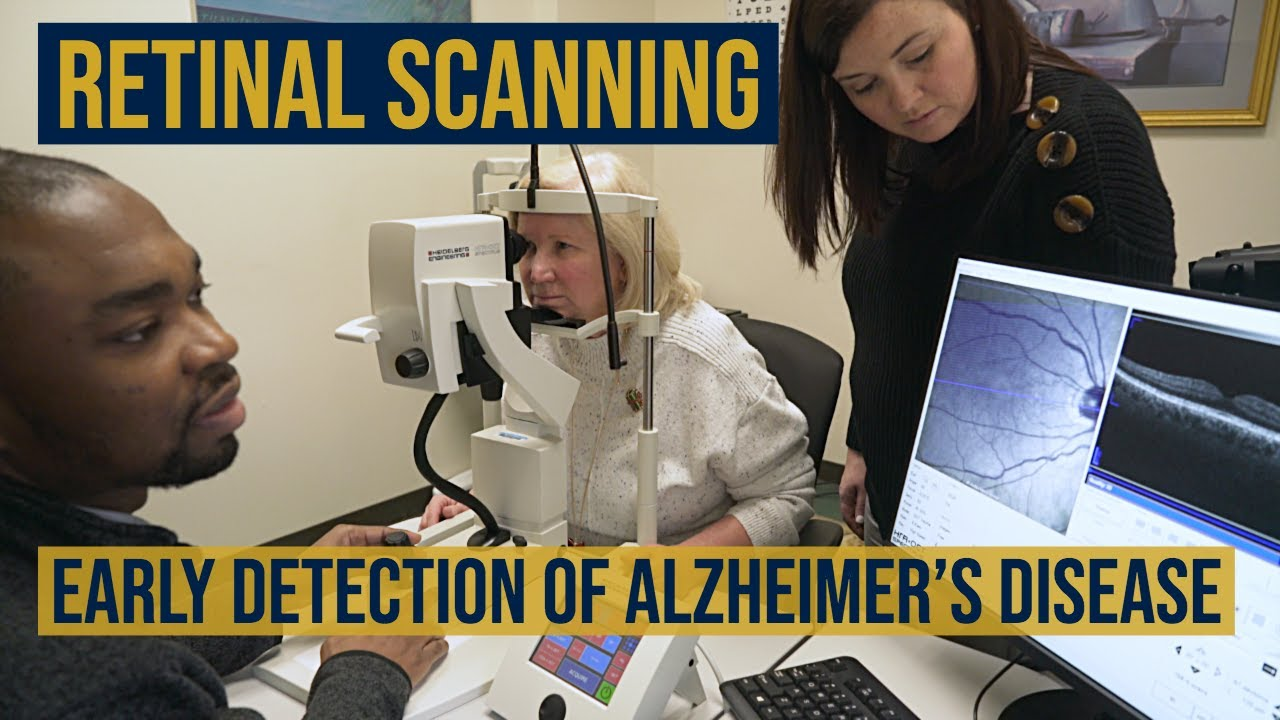
The Alzheimer’s early detection test represents a groundbreaking development in the quest to identify cognitive decline before traditional symptoms arise. Researchers at Harvard-affiliated Mass General Brigham have initiated a pioneering olfactory test that empowers individuals to assess their risk of Alzheimer’s disease from the comfort of their homes. This innovative approach, which requires participants to sniff and identify various odors, highlights the potential for early detection Alzheimer’s technology to transform how we approach neurodegenerative diseases. Initial findings indicate that these tests can distinguish between individuals with cognitive impairment and those who are cognitively healthy, showcasing their effectiveness for Alzheimer’s test applications. As awareness grows around cognitive impairment detection, this at-home solution could pave the way for timely intervention and improved outcomes for millions at risk of Alzheimer’s.
In the ever-evolving landscape of neurological health, early identification of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease has become a pressing focus among researchers and healthcare professionals. A novel home test for Alzheimer’s, designed to evaluate olfactory sensitivity, stands at the forefront of this initiative, offering individuals a proactive way to monitor their cognitive health. By assessing one’s ability to recognize and remember different scents, this test serves as a valuable tool for early detection of Alzheimer’s and related disorders. The significance of such cognitive impairment detection methods cannot be understated, as they provide crucial insights into the onset of neurodegenerative changes. As the medical community aims to expand awareness, solutions like the olfactory home test Alzheimer’s are poised to play a vital role in improving our understanding and management of cognitive conditions.
The Importance of Early Detection in Alzheimer’s Disease
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for improving the quality of life for individuals at risk. Cognitive impairment often develops gradually, and identifying it in its nascent stages allows for early intervention strategies, including lifestyle modifications and potential therapeutic options. By recognizing the warning signs before the substantial memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s appears, individuals can preserve their independence for a longer period and receive support tailored to their needs.
Furthermore, the advancement of screening methods, such as the at-home olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, marks a significant breakthrough in early detection. Utilizing simple tasks that assess an individual’s ability to identify and remember smells provides a non-invasive and cost-effective means to gauge cognitive health. This empowers not only patients but also families and caregivers to be proactive in seeking further evaluation and treatment, which could potentially slow the progression of Alzheimer’s.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Alzheimer’s early detection test?
An Alzheimer’s early detection test, such as the olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, assesses cognitive function and sensory perception, particularly the sense of smell. It aims to identify individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease before any noticeable symptoms appear.
How does the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s work?
The olfactory test for Alzheimer’s involves participants sniffing odor labels on a card to evaluate their ability to identify, discriminate, and remember different smells. This test can be conducted in the comfort of one’s home and has shown promising results in identifying cognitive impairment among older adults.
Why is early detection of Alzheimer’s important?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s is crucial as it allows for timely intervention, which can help slow disease progression and improve quality of life. Tests that identify cognitive impairment, like the olfactory test, enable healthcare professionals to monitor patients and develop tailored treatment plans before significant memory symptoms arise.
Can I perform an Alzheimer’s test at home?
Yes, the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s is designed to be a home test. It provides a simple and noninvasive way for individuals to assess their smell identification capabilities, which may indicate cognitive impairment, and potentially signal early signs of Alzheimer’s.
How effective is the olfactory test in detecting Alzheimer’s?
The olfactory test has shown effectiveness in detecting cognitive impairment among older adults. Research indicates that individuals with mild cognitive impairment score lower on the olfactory test compared to those who are cognitively normal, suggesting its potential value in early Alzheimer’s detection.
What should I do if my Alzheimer’s early detection test results are concerning?
If your Alzheimer’s early detection test results indicate potential cognitive impairment, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. They may recommend further evaluation, including neuropsychological testing, to determine the appropriate next steps for diagnosis and management.
Are cognitive impairment detection tests suitable for all ages?
Cognitive impairment detection tests, including those for early detection of Alzheimer’s, are primarily designed for older adults, as age is a significant risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. However, they can also be adapted for younger populations experiencing cognitive symptoms.
What role do olfactory tests play in Alzheimer’s research?
Olfactory tests play a significant role in Alzheimer’s research, as they provide valuable insights into the early biomarkers of neurodegenerative disease. Studies suggest that changes in smell perception may be an early indicator of Alzheimer’s, making these tests a potential tool for early diagnosis and intervention.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Researchers developed an at-home olfactory test to detect signs of cognitive impairment. |
| The test identifies individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease even before symptoms appear. |
| Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on the test compared to cognitively normal individuals. |
| The study indicates olfactory dysfunction could be a warning sign for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Results were consistent across English- and Spanish-speaking participants, suggesting broad applicability. |
| Future studies may integrate neuropsychological assessments and monitor patients over time. |
Summary
The Alzheimer’s early detection test developed by researchers from Mass General Brigham provides a groundbreaking method to identify individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease years before clinical symptoms manifest. Through innovative olfactory assessments completed in the comfort of home, researchers underscore the potential of scent recognition as an early indicator of cognitive decline. This approach not only holds promise for early intervention strategies but also paves the way for further research aimed at enhancing Alzheimer’s treatment and prevention.