Sugar addiction has become a topic of serious discussion in recent years as increasing numbers of people grapple with overwhelming sugar cravings. While sugar may not fit the strict clinical definition of an addictive substance, many experts are beginning to understand the effects of sugar on our bodies and minds. The easy availability of heavily processed foods laden with added sugar can exacerbate these cravings, leading to unhealthy eating habits. Just as alcohol and nicotine stimulate our brain’s reward centers, the alluring taste of sugary treats can trigger similar responses, leaving individuals feeling dependent on their sweet fix. Understanding the sugar health effects is vital for making informed dietary choices and reducing reliance on these addictive substances.
The phenomenon of sugar dependency is often equated with cravings for other vices like alcohol or cigarettes; however, it is essential to recognize that this lingering desire for sweetness can manifest in various forms. Sugar-rich foods, particularly those designed to be ultra-processed, can create a cycle of compulsive eating that profoundly impacts overall health. The allure of these sweetened products can lead to habitual consumption, complicating personal attempts to reduce intake. With an increasing awareness of the effects of sugar on mental and physical well-being, many individuals seek alternative ways to navigate their relationship with these seemingly innocuous nutrients. Breaking free from the grip of sweetened temptations often necessitates a deeper understanding of one’s eating behaviors and their underlying psychological effects.
Understanding Sugar Addiction: A Complex Debate
The question of whether sugar is truly addictive has sparked widespread debate among nutrition experts. While substances like alcohol and nicotine have clear clinical classifications as addictive, sugar is often considered in a different light. Research shows that sugar can activate the brain’s reward system, triggering cravings similar to those associated with addictive substances. Individuals often find themselves reaching for sugary snacks and beverages, cultivating a cycle of compulsive eating behaviors that can be hard to break. Although these patterns arise, it’s crucial to contextualize them within our broader dietary and biological needs.
Despite the addictive qualities that sugar may exhibit, many nutritionists argue that sugar’s role in our diets is more nuanced. Unlike alcohol or drugs that are considered unnecessary for survival, sugar naturally occurs in fruits, vegetables, and dairy, serving essential nutritional functions. Therefore, while some may experience withdrawal-like symptoms when reducing sugar intake, particularly from highly processed foods, eliminating sugar entirely is virtually impossible without negative implications for overall nutrition. Understanding sugar addiction requires a balanced approach, focusing on moderation rather than complete avoidance.
The Psychological and Physical Effects of Sugar Cravings
Cravings for sugar are not merely psychological; they have physical ramifications as well. When individuals consume high amounts of added sugar, particularly through processed foods, the body can become dependent on that sugar surge. This dependency often leads to withdrawal-like symptoms when intake is reduced. Many people report feeling lethargic, irritable, or experiencing headaches when they limit their sugar consumption, indicating that the body has adapted to a certain level of sugar and reacts negatively to its absence.
Additionally, the effects of sugar are compounded by modern food systems that prioritize convenience and flavor over nutritional value. High sugar foods are often engineered to be hyper-palatable, making them hard to resist. This can potentially lead to eating disorders or long-term health complications such as obesity and diabetes. Understanding the psychological underpinnings of these cravings is essential in crafting better dietary habits that prioritize whole, minimally processed foods over sugary alternatives.
Processed Foods and Their Role in Sugar Addiction
Ultra-processed foods are a significant contributor to sugar addiction, providing convenient yet unhealthy options filled with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These products are designed to be appealing and accessible, effectively increasing sugar consumption among the general populace. When individuals frequently reach for these convenient snacks, their taste buds adjust to expect high levels of sweetness, which can lead to increased cravings for similar products. Over time, this habitual consumption can establish a dependency on these processed foods.
Combatting the influence of processed foods requires a conscious effort to educate ourselves and choose healthier options. Limiting our intake of processed snacks and drinks, while opting for whole foods, can help recalibrate our taste preferences towards naturally sweeter sources of sugar, like fruits. This shift not only improves our overall health and well-being but also aids in breaking the cycle of sugar addiction fostered by processed food options.
The Health Consequences of Excessive Sugar Consumption
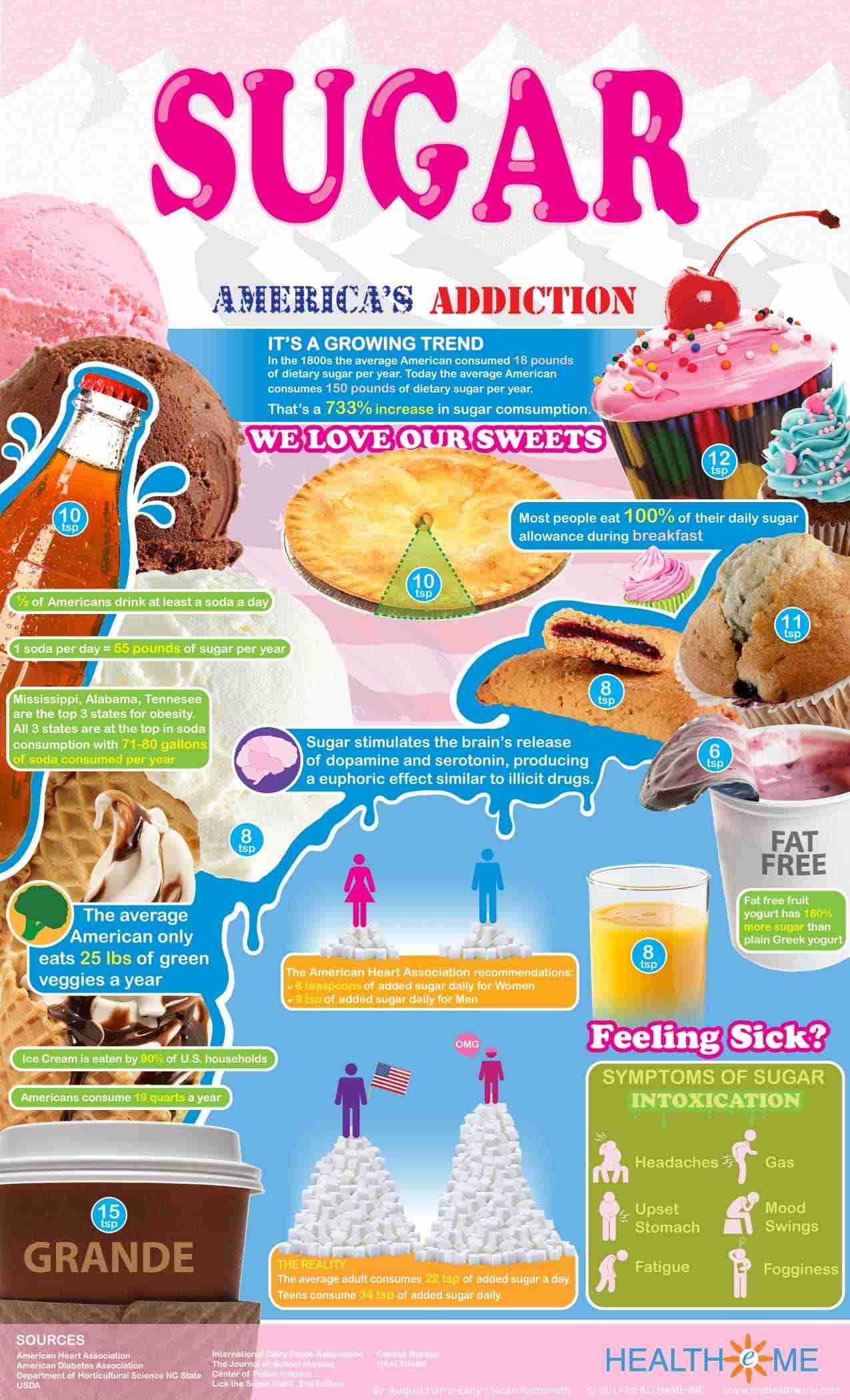
The health effects of sugar are a pressing concern, particularly as average sugar consumption rates continue to rise. Excessive intake of added sugars has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. The American Heart Association suggests strict guidelines for sugar consumption — no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women — which indicates how crucial it is to monitor our intake to avoid these negative health effects. Many underestimate how easily these calories can accumulate, particularly through sugary beverages and snacks.
In addition to physical health consequences, high sugar consumption can also make individuals more susceptible to mental health issues. There is growing evidence that shows a correlation between high sugar intakes and conditions like anxiety and depression. Thus, understanding the full scope of sugar’s potential health effects extends beyond weight management to encompass emotional and psychological well-being. Making informed choices about sugar consumption is vital for achieving and maintaining long-term health.
Navigating Sugar Reduction: Tips and Strategies
Reducing sugar intake can be challenging, especially for those accustomed to large amounts of added sugar in their diets. Experts recommend a gradual approach, starting by identifying and eliminating the most significant sources of added sugars, such as sugary drinks and snacks. Instead, individuals can substitute with healthier alternatives, such as fruits, nuts, or homemade snacks, which provide natural sweetness without added sugars. This strategy not only satisfies cravings but also enhances nutritional intake.
It is also beneficial to read food labels carefully, recognizing where hidden sugars may lurk in your diet. Companies often include added sugars in foods that may not initially seem sweet, such as sauces, dressings, and breads. By becoming mindful consumers and actively choosing products with lower sugar content, individuals can gain better control over their sugar consumption. Adopting these strategies can assist anyone struggling with sugar cravings in cultivating healthier eating habits over time.
The Role of Awareness in Managing Sugar Consumption
Being aware of one’s dietary habits is the first step in managing sugar consumption. Understanding what contributes to sugar addiction and how various foods influence cravings is essential for making informed choices. Nutrition experts emphasize the importance of education on food labels, ingredient lists, and healthy choices. This increase in awareness can empower individuals to take control of their diets rather than falling victim to the marketing tactics of sugary processed foods.
Additionally, fostering a healthy relationship with food, including recognizing when you are hungry versus eating out of habit or emotion, can help individuals understand and mitigate their sugar cravings. Mindfulness practices, such as eating slowly and savoring each bite, can also make a significant difference in sugar consumption patterns. Cultivating awareness around food choices can ultimately lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
The Importance of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
While the conversation around sugar is often dominated by its potential harms, it is important to recognize that sugar does play a role in a balanced diet. Natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients along with energy. These natural forms of sugar also come with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are crucial for overall health. Acknowledging the distinction between natural and added sugars allows individuals to enjoy the health benefits of naturally occurring sugars without the adverse effects tied to excessive added sugar consumption.
In moderation, sugar can enhance the flavor and enjoyment of meals. Striving for balance rather than strict elimination can lead to sustainable eating habits. Nutritionists encourage including naturally sweet foods in diets which can satiate sugar cravings while providing healthier nutritional profiles compared to processed sugary snacks. This balanced approach ensures that people can enjoy sweets without compromising their health.
The Impact of Sugar on Mood and Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a significant link between sugar consumption and mood regulation. High sugar diets can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels that result in mood swings, irritability, and even depressive symptoms. These patterns often perpetuate a cycle where individuals crave more sugar to combat low energy and negative feelings, leading to further consumption and continued emotional turmoil. Understanding this relationship can assist individuals in making more conscious choices about their sugar intake and its potential emotional consequences.
Conversely, reducing high sugar foods can promote better mood stability and emotional well-being. Individuals may experience increased energy levels and improved mental clarity after cutting back on added sugars, helping to break the cycle of sugar-induced mood swings. This highlights the importance of a balanced diet not just for physical health, but also for emotional regulation and support of mental health.
Finding Balance: Integrating Sugar in Healthy Lifestyles
Striking a balance when it comes to sugar consumption is integral to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Rather than viewing sugar as wholly negative, individuals can learn to enjoy it in moderation. Personal health goals and lifestyle choices play a significant role in determining an appropriate level of sugar intake. Learning to incorporate naturally sweet foods into meals while limiting processed sugars can lead to healthier eating practices.
Diverse approaches, including meal planning and preparation, can help create environments where sugary foods are not the default choice. For example, having healthy snacks on hand can reduce the temptation to grab sugary options when hunger strikes. These balanced strategies can create sustainable habits that enable individuals to enjoy their favorite sweet treats without succumbing to unhealthy sugar addiction.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addiction real, and how does it compare to other addictive substances?
While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, research indicates that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The effects of sugar on the brain can mirror those of addictive substances, creating a cycle of sugar cravings, especially from ultra-processed foods high in added sugar. Understanding these effects is important for managing sugar consumption.
What are the effects of sugar on the body that contribute to sugar addiction?
The effects of sugar on the body include increased cravings, withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety when cutting back, and potential negative health impacts from excessive consumption. This is particularly true with added sugars found in processed foods, which can lead to overeating and a cycle of increased sugar cravings.
How do processed foods relate to sugar addiction and cravings?
Processed foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which make them very palatable and can trigger sugar cravings. Consuming these foods frequently can lead to habitual consumption and dependence on sweetened products, perpetuating the cycle of sugar addiction.
What health effects are associated with excessive sugar intake that may be mistaken for sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar intake can lead to a variety of health effects, including weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome. These health issues can create a dependency on sugar to satisfy cravings and provide quick energy, which may resemble symptoms of sugar addiction.
Can reducing sugar intake alleviate symptoms of sugar addiction?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar intake can help alleviate symptoms associated with sugar cravings and withdrawal. Sudden cessation may lead to intense cravings and withdrawal symptoms, so it’s generally recommended to cut back on added sugars in a gradual and mindful way.
What role do sugar health effects play in the perception of sugar addiction?
The health effects of sugar, such as increased cravings and potential weight gain, can influence the perception of sugar addiction. While it may not fulfill all criteria for addiction, the negative impact on health and the body’s response to sugar contribute to a cycle that resembles addiction.
How much sugar is considered excessive in relation to sugar health effects?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children. Consumption above these levels can lead to adverse sugar health effects, including heightened cravings and dependency.
Is it possible to enjoy sugar without developing a sugar addiction?
Absolutely. Enjoying sugar in moderation is key. Incorporating natural sugars from fruits and whole foods while being mindful of added sugars in processed foods can help maintain balance without falling into the cycle of sugar addiction.
What strategies can help manage sugar cravings related to sugar addiction?
To effectively manage sugar cravings, focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, drink plenty of water, practice mindful eating, and gradually reduce your intake of added sugars. Keeping track of your sugar consumption through food labels can also promote healthier choices.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | Cravings for sugar are real but it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Cravings and Withdrawal Symptoms | Consuming high amounts of sugar can lead to cravings. Withdrawal symptoms may include headaches, anxiety, and more when stopped abruptly. |
| Sugar in Diets | Sugar is necessary in moderate amounts and is naturally present in many foods such as fruits and dairy. |
| Recommendations for Sugar Consumption | The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. Most Americans consume significantly more than this. |
| Gradual Reduction | Going cold turkey on sugar may lead to negative effects; gradual reduction is recommended. |
Summary
Sugar addiction is a significant topic within the realm of nutrition and health. While sugar does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol or nicotine, the cravings and compulsive behaviors associated with it are very real for many individuals. Understanding the balance between necessary sugar intake for our diets and the potential for overconsumption is crucial. By being mindful of our sugar consumption and following recommended guidelines, one can enjoy sweetness without falling into the pitfalls of excessive intake.